No matter where you look, there is a consistent message that it is bad to merge cells in Excel; instead, we should use Center Across Selection.
Whenever my friend Richard Sumner posts about his love of merged cells on LinkedIn, he is always met with many replies stating that merging cells is terrible. But here is the thing… in some scenarios, merging is not only better but the only option.
So, in this post, let’s look at three scenarios when we need to merge cells in Excel.
Table of Contents
Watch the video
Merge Cells vs. Center Across Selection
Let’s start by understanding the difference between merging and center across selection. They both display values across multiple cells but achieve it in different ways.
What are merged cells?
To merge cells, click Home > Merge & Center.
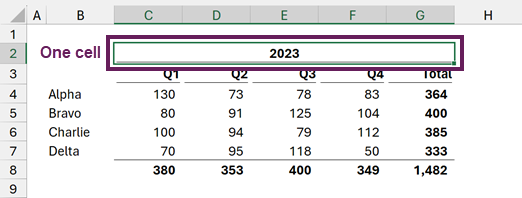
Merging in this way creates a single cell from the selected range. We can change the alignment and formatting of this single cell.
However, this merged cell can lead to issues with:
- Copying and pasting
- Selecting and moving a column of values
- Charts
- Calculations with arrays
- VBA macros
We might even encounter error messages like the following:

What is center across selection?
Center across selection does not create a single cell; instead, it uses cell formatting to display the left cell in the middle of the range.
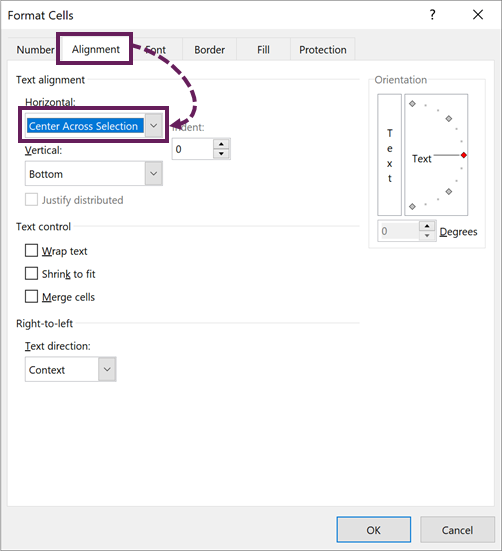
Select the cells to center and press Ctrl + 1
In the Format Cells dialog box, click Alignment > Horizontal (drop down) > Center Across Selection.
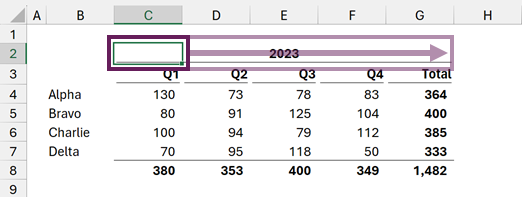
This method keeps all cells separate, but the value in the first cell is displayed as centered across all the other cells.
This does not lead to any of the error messages caused by merge.
When you should merge cells
If center across selection does not trigger any errors, but merged cells do, why should we ever merge cells again?
Well… center across selection is not perfect either. The following three scenarios demonstrate where merging is the better option.
Scenario #1: Grouping & hidden columns
It’s not uncommon for detailed report breakdowns to be hidden inside a group while leaving a total displayed. Users can expand the group and see the complete information if they wish.
Look at the example below. The years are spread across multiple cells.
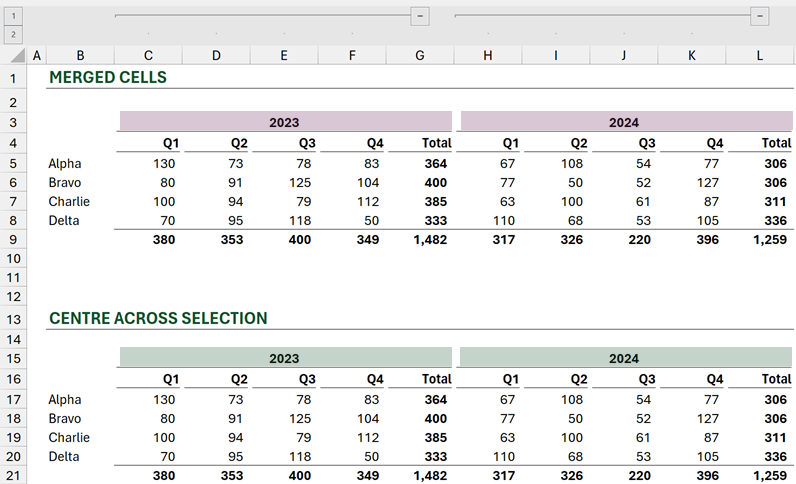
However, what happens if we group or hide the quarterly columns?
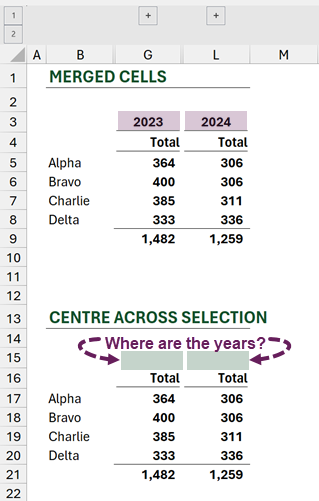
Merge and center correctly displays the year, while center across selection displays a blank cell. So, in this scenario, we need to use a merged cell.
Scenario #2: Merging rows
Center across selection works across columns but not rows. So, let’s suggest we have the following information.
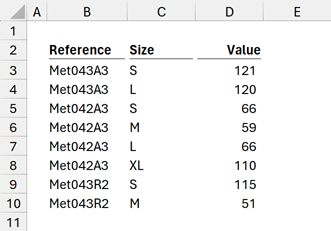
The item numbers are so similar that it’s difficult to see where one ends and another begins. We can’t use center across selection to group the reference numbers, but we can merge cells.
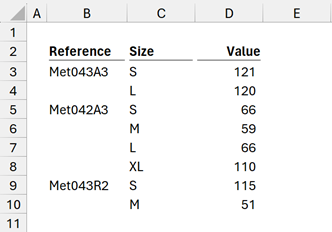
There we go, much better. Cells merged and aligned top and left.
Before anybody says anything… Yes, we can achieve something similar with conditional formatting. The point I’m trying to make is that merged cells can use rows and columns; while center across selection only uses columns.
Scenario #3: Small grid matrix
Look at the following report; something doesn’t look right, does it? Maybe it’s that enormous amount of unused space. The top table has 4 columns; the bottom table has 6.
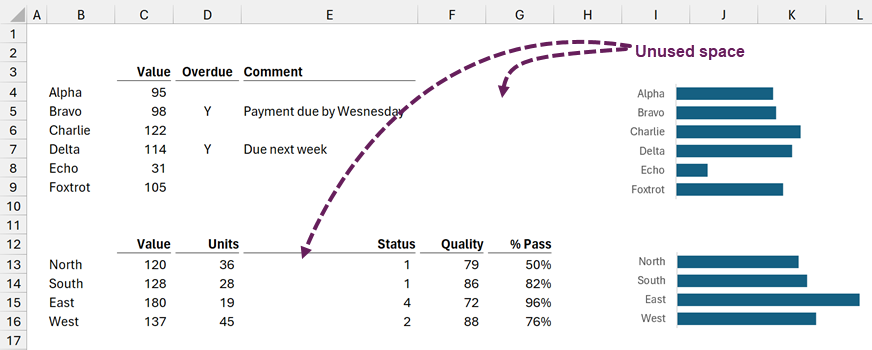
This problem is caused by Excel’s grid structure; everything in the same row/column must have the same height/width. Unless we use a small grid structure.
Look at the image below. There are narrow columns; each cell is a small square. Now, we can fit a 6-column table neatly below a 4-column table.
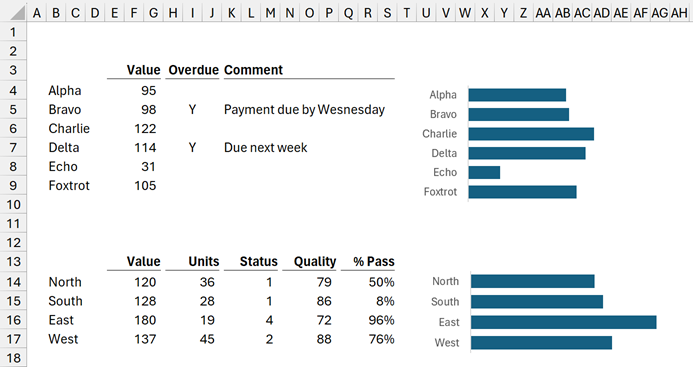
A small grid structure gives the appearance of different columns placed below other columns.
If we still want the freedom to align values how we wish; only merged cells give us this freedom.
Conclusion
All the scenarios in this post involve the presentation of information. This is a crucial distinction to make.
Merged cells should not be used with data or calculations. How data or calculations look is irrelevant; therefore, functionality and avoiding errors is critical.
However, when working on the presentation of a report or input sheet, how something looks is more important. Therefore, we can use merged cells if it provides the options we need.
Related Posts:
- Convert Merged cells to Centre Across Selection with VBA
- VBA code to select all merged cells
- How to make Waffle Charts in Excel: The EASIEST way
Discover how you can automate your work with our Excel courses and tools.

Excel Academy
The complete program for saving time by automating Excel.

Excel Automation Secrets
Discover the 7-step framework for automating Excel.

Office Scripts: Automate Excel Everywhere
Start using Office Scripts and Power Automate to automate Excel in new ways.


MVP Chris Newman shows “How To Add A Center Across Selection Button To Excel’s Home Ribbon Tab” (https://www.thespreadsheetguru.com/center-across-selection-button-to-home-tab/) on his web site. It’s a simple VBA add-in, and I helped him with the XML script to make it appear properly in the ribbon.
Thanks for adding that Jon. That is a good add-in.
Merged cells cause lots of problems in your analysis worksheets, with charts, formulas, etc.
For the display worksheets, the reports, the dashboards, merged cells are just fine, since these should be the final stop on the data to analysis to display journey.
Yep, that is is pretty much my view. The underlying issue is not structuring a workbook properly, but merged cells get the blame.